Quiz 1 the cell and the microscope – Embark on a captivating journey with Quiz 1: The Cell and the Microscope. This comprehensive exploration unveils the fundamental principles of microscopy and its profound impact on our understanding of the cellular realm. Prepare to delve into the intricate world of cells, unraveling their structures, functions, and the historical milestones that shaped our knowledge.
1. Cell and Microscope Basics: Quiz 1 The Cell And The Microscope
The microscope is a fundamental tool in cell biology, allowing scientists to observe and study cells in great detail. Microscopes come in various types, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common type of microscope used in cell biology is the light microscope, which uses visible light to illuminate the specimen.
Electron microscopes, on the other hand, use a beam of electrons to create a much higher resolution image.
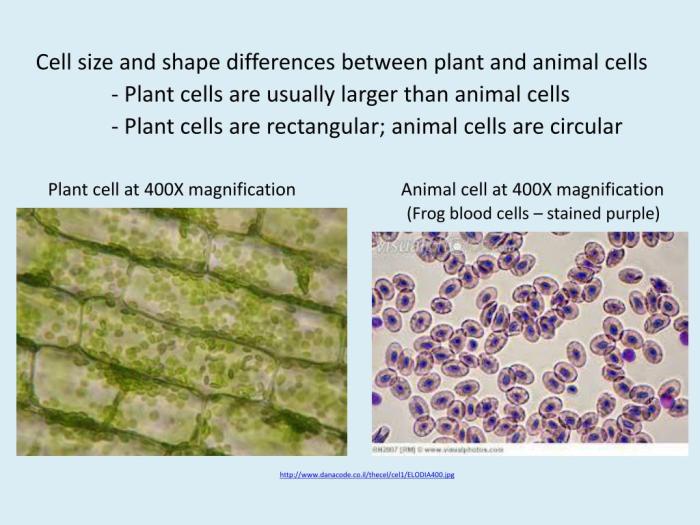
Cells are the basic unit of life, and they come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The smallest cells are prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, and are typically much larger than prokaryotic cells.
2. Microscope Techniques
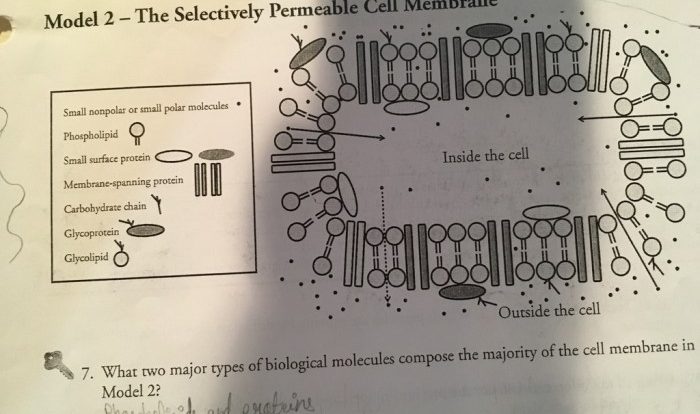
Preparing a wet mount slide for observation is a simple procedure that can be performed in a few minutes. First, a drop of the specimen is placed on a glass slide. A coverslip is then placed over the specimen, and the slide is placed on the microscope stage.
Focusing and adjusting the microscope is essential for obtaining a clear image. The coarse focus knob is used to bring the specimen into approximate focus, and the fine focus knob is then used to fine-tune the focus. The condenser is used to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen, and the diaphragm is used to control the size of the light beam.
Stains and dyes can be used to enhance the visibility of cells and their components. Stains are typically used to color specific structures within the cell, while dyes are used to color the entire cell.
3. Cell Structures and Functions
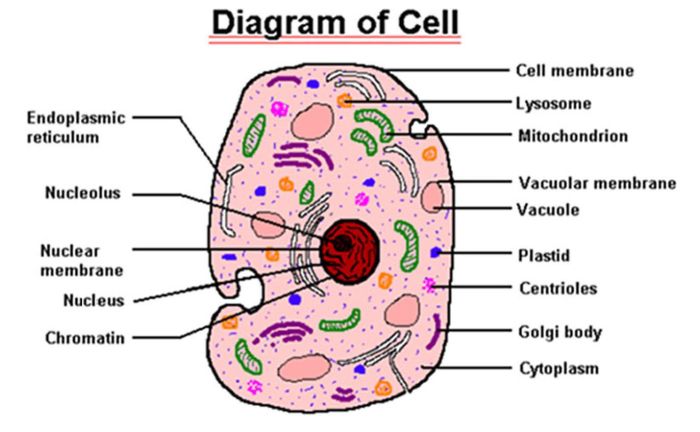
Eukaryotic cells contain a variety of organelles, each with its own specific function. The cell membrane is a thin layer of lipids that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains all of the organelles.
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s DNA. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that modifies and packages proteins. The mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell.
The lysosomes are organelles that contain digestive enzymes that break down waste products.
4. Cell Theory and History
The cell theory is one of the fundamental principles of biology. It states that all living organisms are composed of cells, and that cells are the basic unit of life. The cell theory was first proposed in the 19th century by Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden.
The development of microscopy has played a major role in the development of cell biology. The first microscopes were invented in the 17th century, and they have since been used to make many important discoveries about cells.
5. Applications of Microscopy in Cell Biology
Microscopy is a powerful tool that has been used to make many important discoveries in cell biology. Microscopes have been used to study the structure of cells, the function of cells, and the development of cells. Microscopy has also been used to diagnose diseases and to develop new treatments for diseases.
In the future, microscopy is likely to continue to play an important role in cell biology. Microscopes are becoming more powerful and more affordable, and this is making it possible to study cells in greater detail than ever before.
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the key components of a microscope?
A microscope typically consists of an eyepiece, objective lenses, a stage, a light source, and a condenser.
What is the difference between light microscopy and electron microscopy?
Light microscopy uses visible light to illuminate the specimen, while electron microscopy uses a beam of electrons. Electron microscopy provides much higher resolution than light microscopy.
What are the major organelles found in eukaryotic cells?
The major organelles found in eukaryotic cells include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and vacuoles.
Who is considered the “Father of Microbiology”?
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek is widely regarded as the “Father of Microbiology” for his pioneering work in microscopy and the discovery of microorganisms.