Embark on a scientific odyssey with our comprehensive membrane structure POGIL answer key, meticulously crafted to illuminate the intricacies of cell membranes. This key unveils the composition, arrangement, and diverse functions of membrane proteins, providing a detailed blueprint of the membrane’s architecture.
Delve deeper into the factors that govern membrane fluidity, exploring its critical role in cellular processes. Discover the mechanisms and regulation of membrane transport, unraveling the secrets of nutrient uptake and waste removal. Finally, grasp the concept of membrane potential, understanding its contribution to cell signaling and electrical excitability.
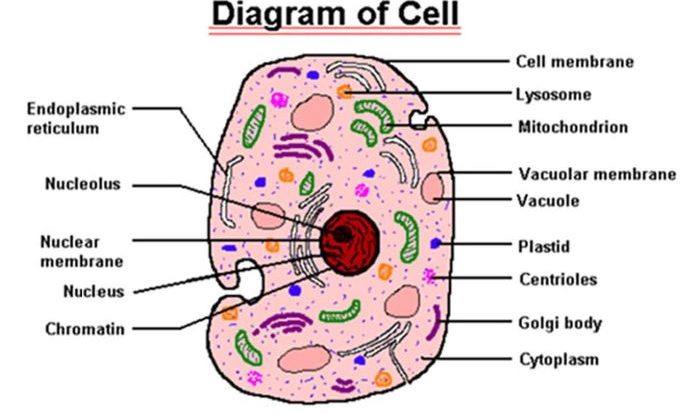
Membrane Structure
The plasma membrane is a complex structure that forms the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is a double layer of phospholipids. Phospholipids are molecules that have a hydrophilic (water-loving) head and a hydrophobic (water-hating) tail.
The hydrophilic heads face outward, toward the aqueous environment inside and outside the cell, while the hydrophobic tails face inward, away from the water.In addition to phospholipids, the plasma membrane also contains proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol. Proteins are the most abundant component of the membrane, and they perform a variety of functions, including transport, signaling, and adhesion.
Carbohydrates are attached to the proteins and lipids in the membrane, and they help to protect the cell from damage. Cholesterol is a type of lipid that helps to maintain the fluidity of the membrane.The plasma membrane is a dynamic structure that is constantly changing.
It is constantly being remodeled by the addition and removal of lipids and proteins. This remodeling is essential for the cell to maintain its homeostasis and to respond to changes in its environment.
Membrane Fluidity
The fluidity of the plasma membrane is essential for its function. A fluid membrane allows for the movement of proteins and lipids within the membrane, and it also allows for the passage of molecules across the membrane. The fluidity of the membrane is controlled by a number of factors, including the temperature, the composition of the membrane, and the presence of membrane-associated proteins.The
temperature of the membrane affects its fluidity. As the temperature increases, the membrane becomes more fluid. This is because the increased temperature causes the phospholipids in the membrane to move more rapidly, which disrupts the interactions between them.The composition of the membrane also affects its fluidity.
Membranes that contain a high proportion of unsaturated phospholipids are more fluid than membranes that contain a high proportion of saturated phospholipids. Unsaturated phospholipids have kinks in their tails, which prevents them from packing together as tightly as saturated phospholipids.
This results in a more fluid membrane.Membrane-associated proteins can also affect the fluidity of the membrane. Some proteins, such as integral membrane proteins, span the entire membrane. These proteins can restrict the movement of phospholipids and other molecules within the membrane, which can make the membrane less fluid.
Other proteins, such as peripheral membrane proteins, are attached to the surface of the membrane. These proteins can increase the fluidity of the membrane by disrupting the interactions between phospholipids.
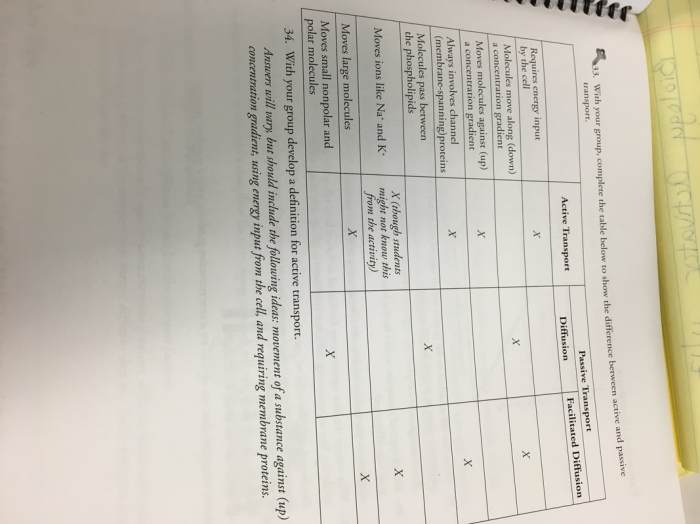
Membrane Transport
The plasma membrane is a selectively permeable barrier, which means that it allows some molecules to pass through it while blocking others. The passage of molecules across the membrane is essential for the cell to maintain its homeostasis and to respond to changes in its environment.There
are a number of different mechanisms by which molecules can cross the plasma membrane. These mechanisms include:
- Simple diffusion
- Facilitated diffusion
- Active transport
- Endocytosis
- Exocytosis
Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. This type of transport does not require energy. Facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules across a membrane with the help of a membrane-associated protein.
This type of transport also does not require energy. Active transport is the movement of molecules across a membrane against a concentration gradient. This type of transport requires energy. Endocytosis is the process by which the cell takes in material from its surroundings.
This process involves the formation of a vesicle that engulfs the material and then transports it into the cell. Exocytosis is the process by which the cell releases material from its surroundings. This process involves the formation of a vesicle that fuses with the plasma membrane and then releases its contents outside the cell.
Membrane Potential, Membrane structure pogil answer key
The plasma membrane is polarized, which means that it has a difference in electrical charge across it. The inside of the cell is negative relative to the outside of the cell. This difference in charge is called the membrane potential.The
membrane potential is generated by the movement of ions across the membrane. Ions are atoms or molecules that have a net electrical charge. The most important ions for the generation of the membrane potential are sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), and chloride (Cl-).Sodium
ions are more concentrated outside the cell than inside the cell. Potassium ions are more concentrated inside the cell than outside the cell. Chloride ions are more concentrated outside the cell than inside the cell.The movement of these ions across the membrane is controlled by ion channels.
Ion channels are proteins that span the membrane and allow ions to pass through. The opening and closing of ion channels is controlled by a variety of factors, including the voltage across the membrane, the concentration of ions on either side of the membrane, and the presence of ligands.The
membrane potential is essential for a variety of cell functions, including nerve conduction, muscle contraction, and the regulation of cell volume.
Detailed FAQs: Membrane Structure Pogil Answer Key
What is the primary function of the plasma membrane?
The plasma membrane serves as a selective barrier, regulating the passage of molecules into and out of the cell.
How does membrane fluidity contribute to cell function?
Membrane fluidity allows for the movement of membrane proteins, enabling essential cellular processes such as signal transduction and nutrient uptake.
What factors influence membrane transport?
Factors influencing membrane transport include concentration gradients, membrane permeability, and the presence of transport proteins.