Student exploration determining a spring constant sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
This exploration delves into the fascinating world of springs, where students embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of these seemingly simple yet remarkable devices. Through hands-on experimentation and meticulous data analysis, they will uncover the fundamental properties of springs, gaining a deeper understanding of their behavior and applications.
Student Exploration Determining a Spring Constant
Student exploration is a valuable approach to fostering scientific inquiry and problem-solving skills. In this exploration, students determine the spring constant of a spring through hands-on experimentation. Understanding the spring constant is crucial in comprehending the behavior of springs and has applications in various fields.
Materials and Equipment
- Springs with varying characteristics (size, shape, material)
- Weights with known masses
- Rulers or measuring tapes
- Force sensors or dynamometers
Experimental Design, Student exploration determining a spring constant
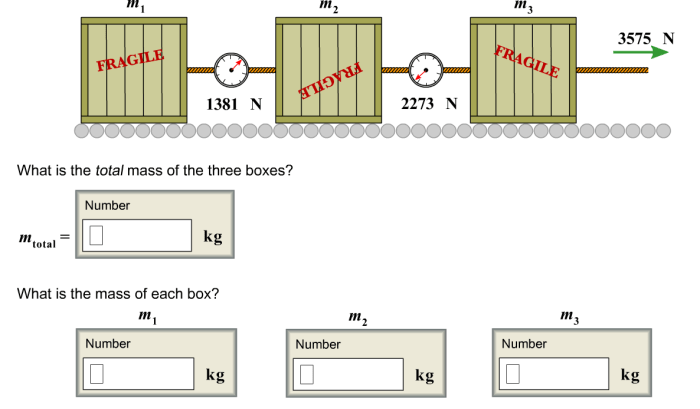
The experimental setup involves attaching a weight to the spring and measuring the resulting displacement. The force applied is calculated based on the weight’s mass and the acceleration due to gravity. By varying the applied force and measuring the corresponding displacement, students can establish a relationship between force and displacement.
Data Analysis
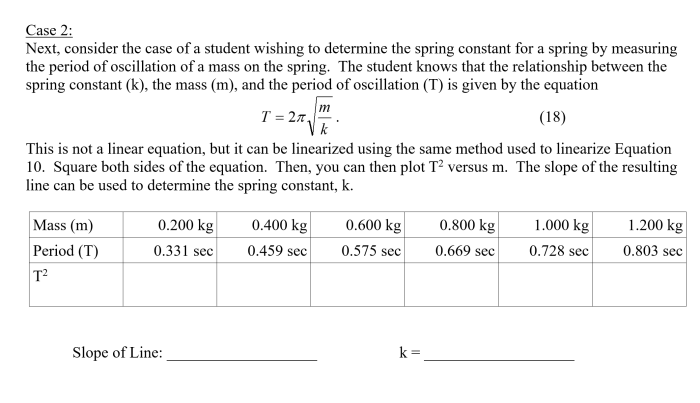
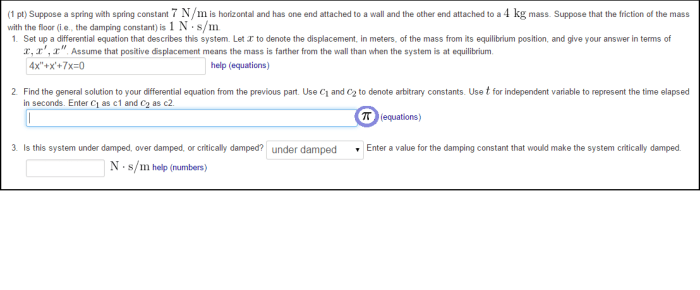
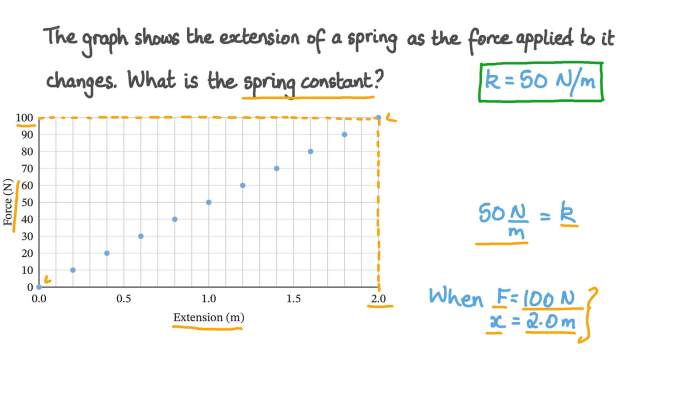
The relationship between force ( F), displacement ( x), and spring constant ( k) is given by Hooke’s law: F =-kx . Using this equation, students can calculate the spring constant by plotting a graph of force versus displacement and determining the slope of the line.
Potential sources of error include measurement inaccuracies, friction, and non-ideal spring behavior. To minimize these errors, careful measurement techniques, appropriate equipment calibration, and multiple trials are recommended.
Discussion
The spring constant is a measure of the stiffness of a spring. A higher spring constant indicates a stiffer spring that requires more force to deform. Factors affecting the spring constant include the material properties (Young’s modulus) and geometry (length, cross-sectional area) of the spring.
Understanding the spring constant is crucial in designing and analyzing systems involving springs, such as shock absorbers, suspension systems, and energy storage devices.
Essential FAQs: Student Exploration Determining A Spring Constant
What is the purpose of determining a spring constant?
Determining a spring constant allows us to quantify the stiffness of a spring, which is a crucial parameter for understanding its behavior under various forces and displacements.
How is a spring constant calculated?
The spring constant is calculated by dividing the force applied to the spring by the resulting displacement. This relationship is known as Hooke’s law.
What factors can affect the spring constant?
The spring constant can be influenced by various factors, including the material properties of the spring, its geometry (length, diameter, shape), and any pre-existing stresses or deformations.