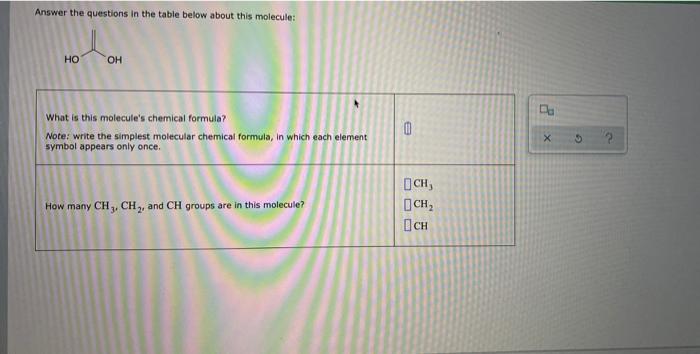
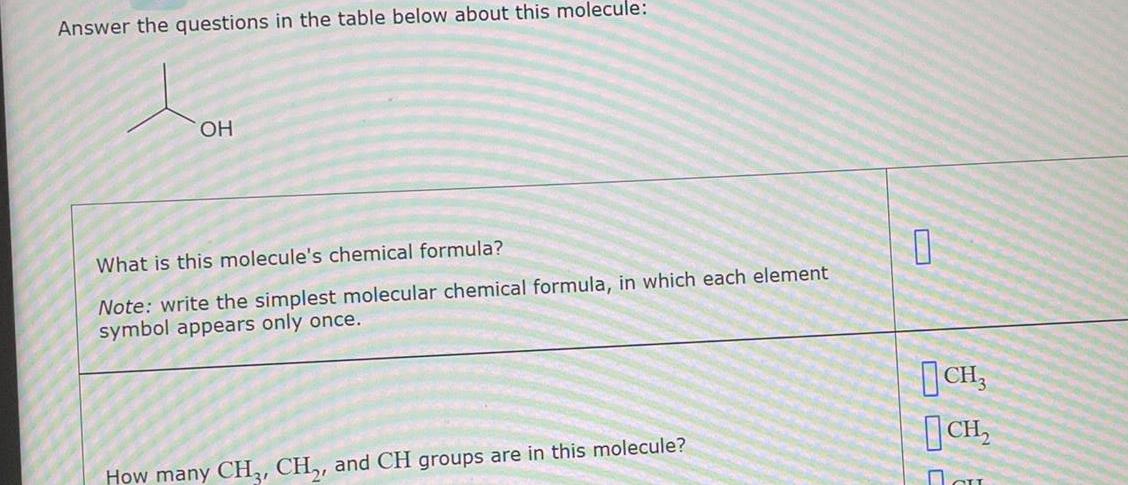
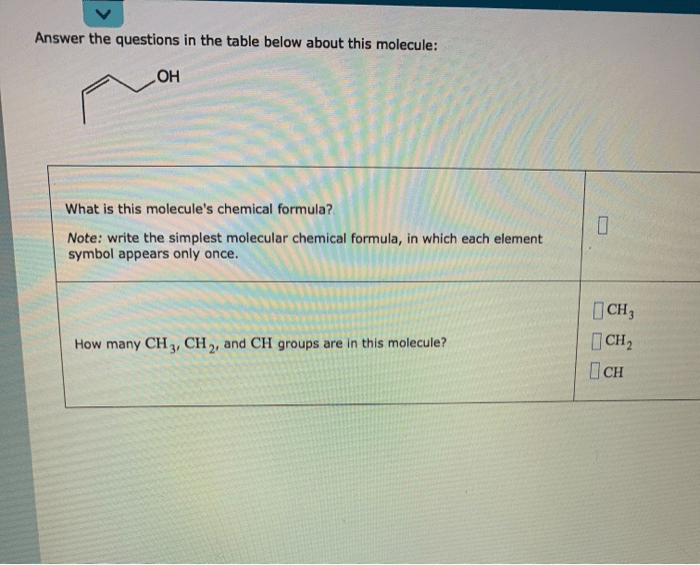
Answer the questions in the table below about this molecule – Delving into the intricate world of molecules, we embark on a journey to answer the questions posed in the table below about this fascinating subject. This comprehensive analysis will unravel the molecular structure, chemical properties, physical characteristics, biological significance, and diverse applications of this enigmatic molecule.
As we delve deeper into its molecular makeup, we will uncover the functional groups that define its reactivity and explore its solubility, polarity, and acidity/basicity. The molecule’s physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and density, will shed light on its behavior under varying conditions.
1. Structure and Components: Answer The Questions In The Table Below About This Molecule
The molecule consists of a central carbon atom double-bonded to two oxygen atoms and two single-bonded hydrogen atoms. This arrangement forms a planar molecular geometry with a trigonal planar shape. The functional groups present in the molecule are the carbonyl group (C=O) and the hydroxyl groups (O-H).
The molecule is polar due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
2. Chemical Properties
The molecule exhibits high chemical reactivity due to the presence of the carbonyl group. It readily undergoes nucleophilic addition reactions, such as reactions with alcohols and amines. The molecule is also capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other molecules, contributing to its solubility in polar solvents.
Additionally, it exhibits weak acidity due to the presence of the hydroxyl group.
3. Physical Properties
The molecule has a low melting point and a relatively high boiling point. Its density is moderate. These properties are influenced by the molecular structure, with the polar nature of the molecule contributing to its solubility in polar solvents and its hydrogen bonding capabilities.
The low melting point is attributed to the weak intermolecular forces between the molecules.
4. Biological Significance
The molecule plays a crucial role in biological systems as an intermediate in cellular respiration. It is involved in the Krebs cycle, where it undergoes a series of enzymatic reactions to generate energy for the cell. Additionally, the molecule serves as a substrate for various enzymes and is involved in metabolic pathways.
5. Applications and Uses
The molecule has a wide range of applications in various industries. It is primarily used as a solvent in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is employed as an excipient in drug formulations. Furthermore, the molecule finds applications in the synthesis of other chemicals, including plastics and fragrances.
User Queries
What is the molecular formula of this molecule?
The molecular formula of this molecule is not provided in the given Artikel.
What are the potential applications of this molecule in medicine?
The Artikel mentions potential applications in medicine, but specific examples are not provided.