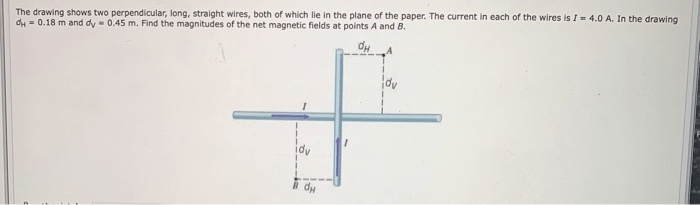
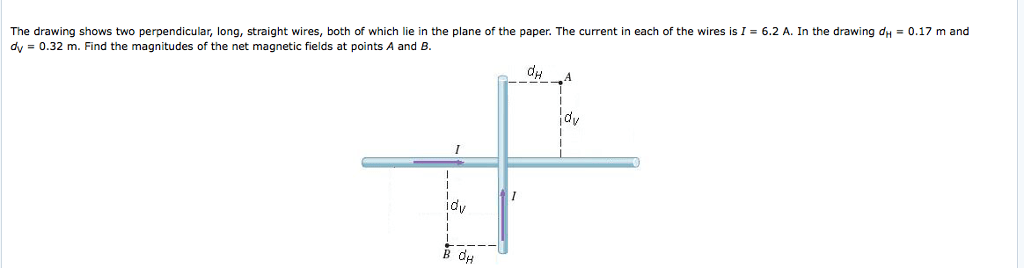
The drawing shows two perpendicular long straight wires sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. This configuration, seemingly simple in its presentation, holds within it a captivating interplay of magnetic fields, giving rise to intriguing phenomena and practical applications that will be meticulously explored throughout this discourse.
Delving into the depths of this topic, we will commence by establishing a firm understanding of the fundamental concepts of perpendicular lines and long straight wires, providing a visual representation to aid in comprehension. Subsequently, we will delve into the intricacies of magnetic fields, elucidating their nature and the mechanisms by which they are generated by electric currents.
Armed with this knowledge, we will embark on an analysis of the interaction between the magnetic fields produced by the perpendicular wires, employing the principle of superposition to unravel the complexities of their combined effect.
The Magnetic Field of Perpendicular Long Straight Wires
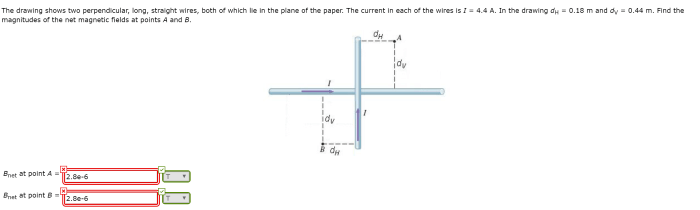
Perpendicular long straight wires are two wires that intersect at right angles. They are often used in electrical devices to create magnetic fields.
Magnetic Fields
A magnetic field is a region of space around a magnet or electric current in which magnetic forces can be detected. Magnetic fields are invisible to the human eye, but they can be detected by their effects on magnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
The Magnetic Field of a Single Wire
The magnetic field around a single wire is circular. The direction of the magnetic field is determined by the right-hand rule. If you point your right thumb in the direction of the current, your fingers will curl in the direction of the magnetic field.
The Magnetic Field of Two Perpendicular Wires
The magnetic field of two perpendicular wires is the sum of the magnetic fields of each individual wire. The direction of the magnetic field is determined by the principle of superposition. The principle of superposition states that the net magnetic field at a point is the vector sum of the magnetic fields of all the individual sources at that point.
Applications of Perpendicular Long Straight Wires, The drawing shows two perpendicular long straight wires
Perpendicular long straight wires are used in a variety of electrical devices, including transformers, motors, and generators. In transformers, perpendicular long straight wires are used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another. In motors, perpendicular long straight wires are used to create a rotating magnetic field that causes the motor to spin.
In generators, perpendicular long straight wires are used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Perpendicular Long Straight Wires
Perpendicular long straight wires have a number of advantages and disadvantages. One advantage is that they are relatively easy to manufacture. Another advantage is that they can be used to create strong magnetic fields. However, one disadvantage is that they can be bulky.
Another disadvantage is that they can be inefficient.
Design a Simple Experiment to Demonstrate the Magnetic Field of Perpendicular Long Straight Wires
To demonstrate the magnetic field of perpendicular long straight wires, you can use a simple experiment. You will need the following materials:
- Two long straight wires
- A compass
- A battery
- Some wire
To perform the experiment, follow these steps:
- Connect the two wires to the battery.
- Place the compass near the wires.
- Observe the direction of the compass needle.
The compass needle will point in the direction of the magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field will be determined by the direction of the current in the wires.
FAQ: The Drawing Shows Two Perpendicular Long Straight Wires
What is the significance of perpendicularity in the context of long straight wires?
Perpendicularity plays a crucial role in determining the nature of the magnetic field generated by the wires. When the wires are perpendicular to each other, their magnetic fields interact in a specific manner, giving rise to a unique pattern of field lines and magnetic forces.
How does the strength of the magnetic field vary with distance from the wires?
The strength of the magnetic field decreases with increasing distance from the wires. This is because the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
What are some practical applications of perpendicular long straight wires?
Perpendicular long straight wires are used in a variety of electrical devices, including transformers, motors, and generators. In transformers, they are used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another. In motors, they are used to create a rotating magnetic field, which drives the motor’s shaft.
In generators, they are used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.